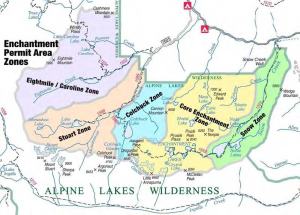
After spending more than three years and a million taxpayer bucks, Chelan County and the Washington Department of Ecology have finally put out an environmental scoping request for the Icicle Work Group’s “Icicle Strategy.” This document identifies our government’s plan to further dam and drain several lakes in the Alpine Lakes Wilderness area for future consumption by Wenatchee Valley developers and irrigators.
Complete details about the impact of the project can be found in the Alpine Lakes Protection Society’s (ALPS) latest newsletter.
People who care about the Alpine Lakes Wilderness – one of America’s most beautiful and popular wilderness areas – need to speak up. Comments regarding the scope of the environmental impact statement must be received by May 11, 2016:
- Mike Kaputa, Director, Chelan Co. Natural Resources Dep’t
- Via e-mail: mike.kaputa@co.chelan.wa.us
- Via snail mail: 411 Washington St., Suite 201, Wenatchee, WA
The SEPA checklist and various descriptions of the Icicle Work Group’s proposal are posted on Chelan County’s website. Here are a few observations that may guide comments.
The Icicle Work Group is a self-appointed conglomeration of government agencies (federal, state, local, tribal), water resource users (irrigators and municipal water suppliers), and a couple of environmental groups interested in getting contracts to do projects. The IWG has no members who are advocating to protect the Alpine Lakes Wilderness.*
The IWG’s “guiding principles” establish that whatever comes out of the process must be a “quid pro quo” deal. Thus, any benefit to the environment will be accomplished only if new water rights are created to fuel development and sprawl in and around the City of Leavenworth, Cashmere, Dryden, etc. These water rights will extract water from the Alpine Lakes Wilderness: Eightmile, Colchuck, Klonaqua, Nada, Snow, and Square Lakes. To obtain this water, the cities will have to build dams and other infrastructure, and will inundate Wilderness lands as well as draw down the Wilderness lakes. You can read the details in the Alpine Lakes Optimization & Automation Study (Table 6, p. 62 provides a handy summary.)
The Icicle Work Group asserts that this plan is environmentally beneficial because it will improve instream flows in Icicle Creek. This assertion is (largely) false. There will be minor improvements to streamflow, but most of the water promised to Icicle Creek is interruptible – that is – in water-short years the cities and irrigators will be able to take their full allotments of water regardless of how little is flowing in the creek. There will not be enough water to protect the endangered steelhead and bull trout that inhabit Icicle Creek.
More analysis of these problems may be found in prior Naiads posts, such as Icicle Instream Illusions, and New Dams and Diversions in the Alpine Lakes Wilderness.
Here’s what the IWG needs to hear:
- The EIS must consider a Wilderness Protection Alternative. This alternative would promote wilderness values as set forth in the Wilderness Act of 1964, would not allow new water infrastructure or diversions inside the Alpine Lakes Wilderness, and would require all new water supply to be obtained outside the Alpine Lakes Wilderness.
- The EIS must consider a Water Conservation Alternative. This alternative would assess using aggressive water conservation measures by Wenatchee Valley cities, including restrictions on lawn watering (as the citizens of Seattle have learned to do). This alternative should also assess transfer of water rights from irrigation districts to cities, where orchards have already been torn out and replaced with residential subdivisions. This alternative should also assess agricultural irrigation efficiency, such as replacing open gravity canals with pipes and pumps and other 21st century concepts. A proposed Conservation Alternative is linked here.
- The EIS must consider an Irrigation District Water Right Change Alternative, which would fix Icicle Creek’s low flow problem. This alternative would evaluate moving the Icicle-Peshastin Irrigation District’s water right diversion, which presently takes 100 cubic feet per second out of Icicle Creek, to the Wenatchee River downstream about 3 miles. This measure, which would permanently fix Icicle Creek’s low flow problem, would convert the IPID diversion from gravity flow to pumping (requiring electrical power). The Icicle Work Group should therefore analyze renewable energy options to supply that power, including solar, wind and in-canal hydroelectric.
- The EIS must consider a Water Right Relinquishment Alternative. Removal of water from the Alpine Lakes Wilderness is on the table only because IPID holds water rights that were grandfathered when the Wilderness was created. And – as IPID will tell anyone who will listen – every year they use what they need. When the dam at Eightmile Lake fell down decades ago they didn’t fix it because they did not need more water. When a party doesn’t use their rights, they lose them. “Use It Or Lose It” – the basic rule of western water law – is controlling. The EIS needs to analyze this.
The IWG’s plan to exploit the Alpine Lakes Wilderness is a camel’s-nose-under-the-tent proposal. As climate change alters the hydrology of the western U.S., we can expect to see many attempts to expand water projects that were grandfathered into wilderness areas. Wilderness advocates need to weigh in by May 11, for the sake of Alpine Lakes and for wilderness values in general.
__________________________
*The Alpine Lakes Wilderness Society (ALPS) was invited and declined to participate. The Center for Environmental Law & Policy (CELP) participated in IWG meetings for two-plus years and then resigned when the operating procedures were changed to gag CELP’s objection to wilderness water projects.